Throughout 2022 and early 2023, Indian refineries purchased Russian crude through Dubai-based intermediaries such as Hinera Trading, Black Pearl Energy Trading, Starex Trading, and Pontus Trading, as well as Dubai-based proxies for Russian NOCs Everest Energy, DMCC and Lukoil Litasco.
Indian rupees were utilized to bypass SWIFT for Russian oil payments, resulting in Russia accumulating surplus rupees in vostro accounts within India. By mid-2023, Russia ceased accepting rupees for energy trade, leading private Indian refiners to pay for Russian oil in Chinese Yuan while state-owned refiners paid in UAE Dirhams.
In 2024, the threat of U.S. sanctions complicated UAE Dirham transactions, consolidating the dominance of only three middlemen—Lukoil Litasco Middle East, Hinera Trading, and Black Pearl Energy Trading—as primary sellers of Russian crude to India.
A blog focused on educating global physical energy commodities participants on evolving financial, regulatory and marketing developments in the Asian commodities markets including use of cryptocurrencies in physical commodities trading. This blog seeks to educate market participants only and does not constitute financial advice.
Showing posts with label Russia. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Russia. Show all posts
Tuesday, 8 April 2025
Monday, 15 August 2022
New paradigm shift in India’s energy trade - evidence in charts
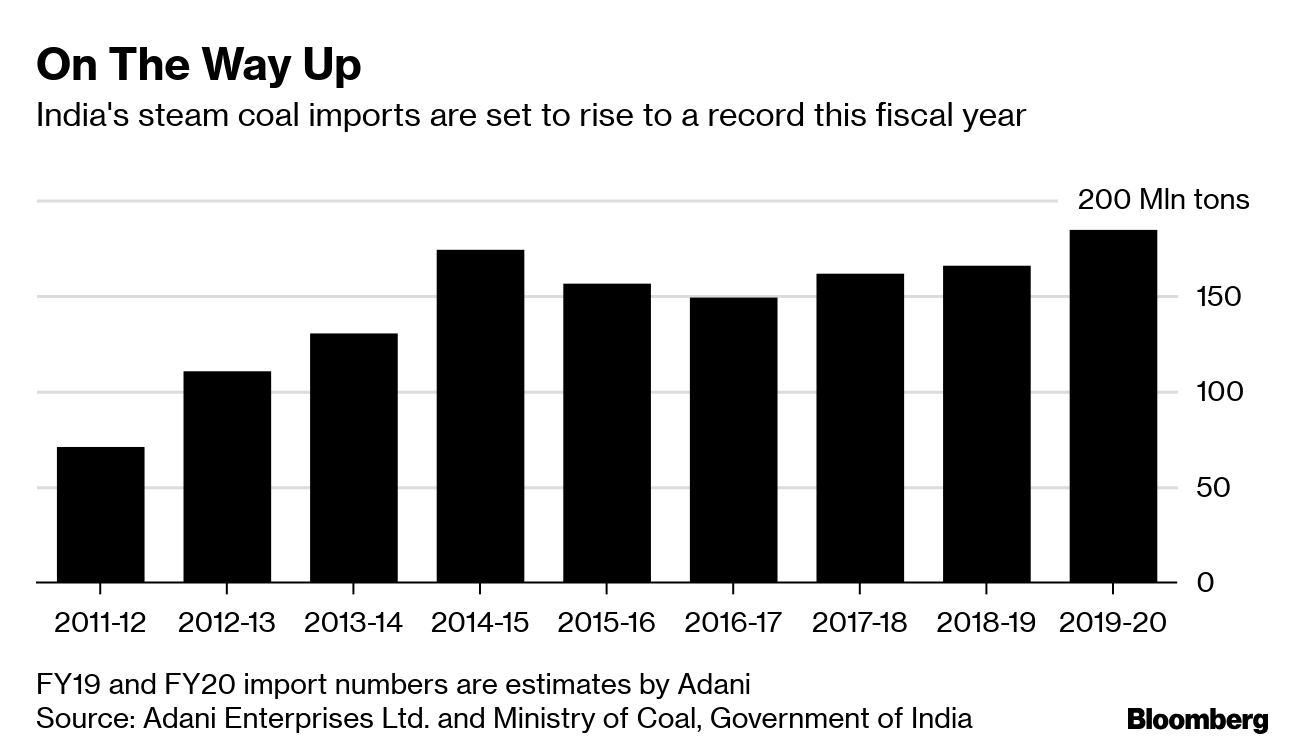
An unprecedented paradigm shift is evolving in the energy commodities trade of India, the world’s third-largest oil consumer after the US and China, and second largest oil importer after China importing over 85 percent of its crude needs. Despite being the second largest coal producer in the world, India is also the world’s second largest coal importer as new power plants designed to use only high grade imported coal (17.6 GW or 8.6% of the 204.9 GW installed power generation capacity) while older power plants import the fuel for blending with domestic coal according to S&P Global. Indian Ministry of Commerce’s Export & Import Data Bank (EIDB) points to crude oil imports worth US$ 122.45 billion and around 173.32 million tons of coal imports worth US$ 30.6 billion in the year 2021-22.
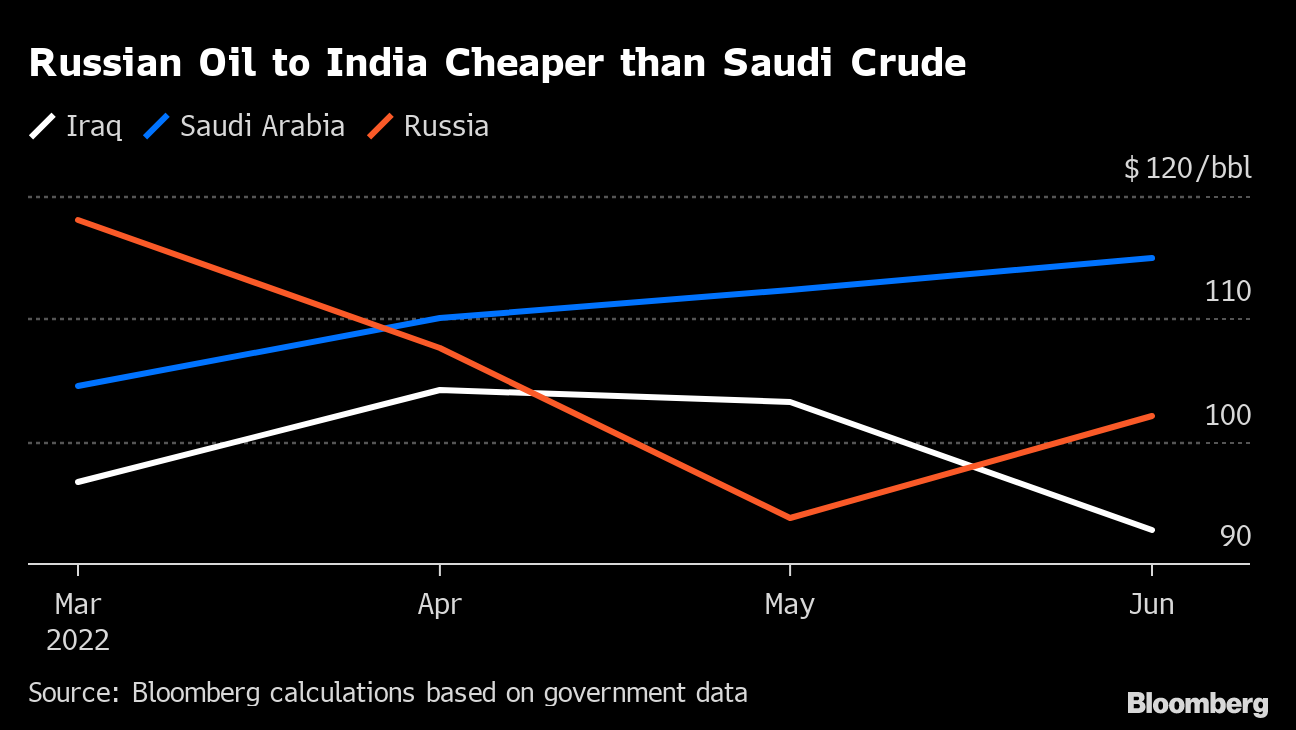
In a new paradigm shift, according to analysis by Bloomberg, Russia surpassed Saudi Arabia as the second-biggest supplier of crude to India in June 2022, ranked just behind Iraq.
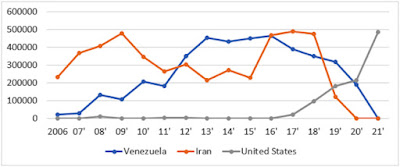
In comparison, India’s imports of U.S. oil and gas commodities which grew from $4.1 billion in 2018 to $5.5 billion in 2020 roughly halved by July 2021 and the US is no longer among India’s top oil suppliers according to the oil ministry’s Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell.
With economic growth expected to rise to 8% this year, Indian state refiners which dominate fuel retailing are in the market for the lowest priced crude that works with their refinery and product configurations via open tenders. The discount of Russian Urals crude to Brent crude was around $30 per barrel with bigger discounts to other medium-sour grades typically sold to India such as Oman and Upper Zakum reflecting the huge risk premium the market requires to transact on Russian cargoes according to Kpler. In 2021, only around 2% of India’s total oil imports (12 million barrels or 33,000 barrels a day on average of Urals crude) came from Russia, according to Kpler.
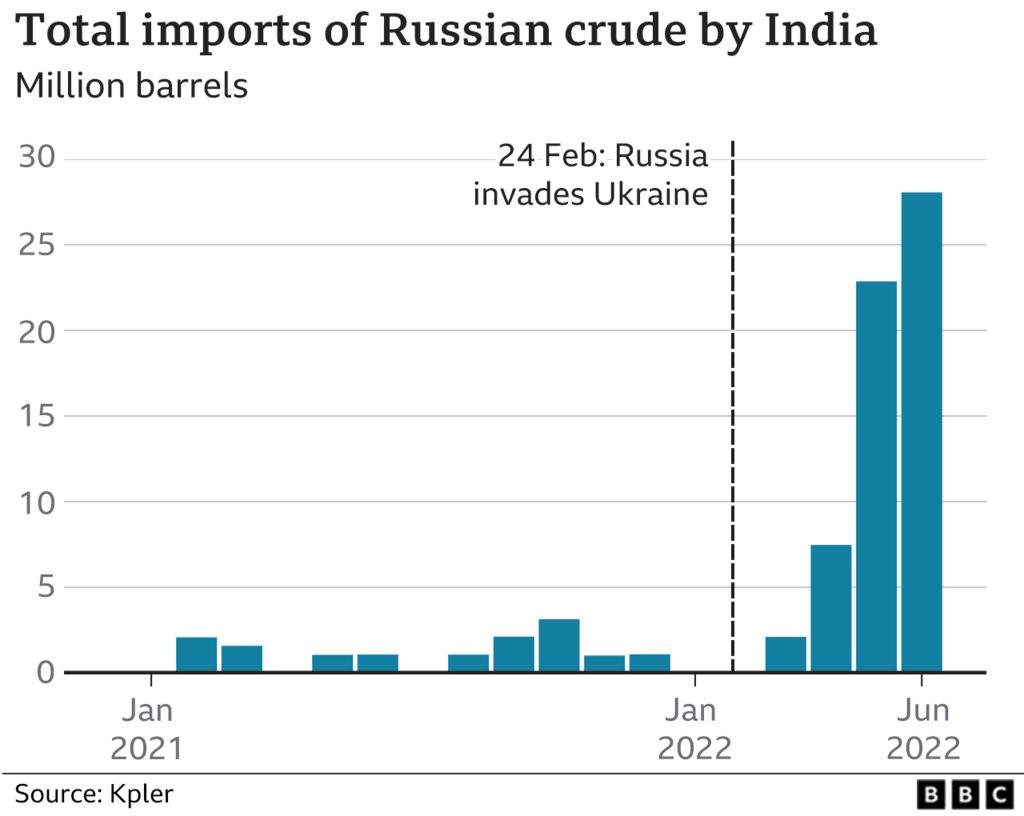
Urals oil contracts for India rose from nothing in January 2022 to 300,000 barrels a day in March to 700,000 a day in April totaling around 26 million barrels ending June 2022 according to Kpler. The India-bound Russian tankers head into Jamnagar, in the western state of Gujarat, where Reliance Industries has the world’s largest refinery complex, and into the Vadinar refinery of Nayara Energy an affiliate of Rosneft, the Russian state company which alone imports crude oil worth about $1bn every month or 400,000 barrels per day on average.
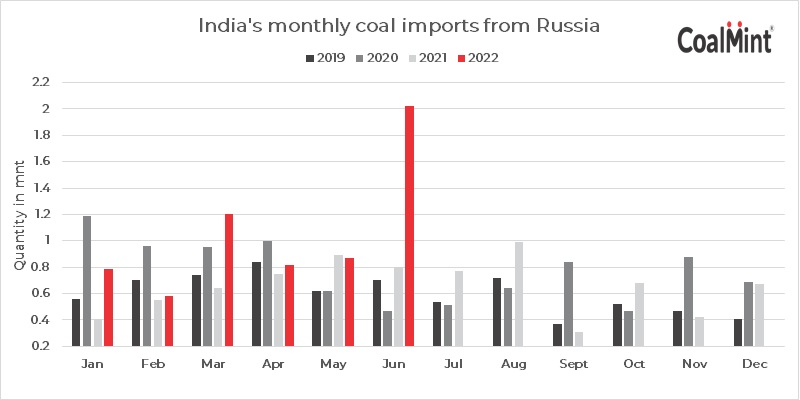
This paradigm shift in India’s energy trade is not limited to oil. Russia became India's third-largest coal supplier in July 2022 after Indonesia and Australia, with imports from Russia jumping 70.3% to a new record of 2.06 million mt, per Coalmint data. In comparison, thermal coal imports from the US fell 52% on the year to 3.4 million mt over the same time. Russian imports to India are expected to rise even higher due to a wider coal shortage during the third quarter of 2022 exacerbated by higher electricity demand. Steep discounts offered by Russian suppliers for thermal coal and Urals crude as global prices trade at near-record highs due to western sanctions are not the only reason for this paradigm shift. India is also exploring alternative payment channels for trade with Russia including allowing payments for energy commodities in the Indian rupee or settling the trade in other Asian currencies furthering this new paradigm.
This paradigm shift in India’s energy trade is not limited to oil. Russia became India's third-largest coal supplier in July 2022 after Indonesia and Australia, with imports from Russia jumping 70.3% to a new record of 2.06 million mt, per Coalmint data. In comparison, thermal coal imports from the US fell 52% on the year to 3.4 million mt over the same time. Russian imports to India are expected to rise even higher due to a wider coal shortage during the third quarter of 2022 exacerbated by higher electricity demand. Steep discounts offered by Russian suppliers for thermal coal and Urals crude as global prices trade at near-record highs due to western sanctions are not the only reason for this paradigm shift. India is also exploring alternative payment channels for trade with Russia including allowing payments for energy commodities in the Indian rupee or settling the trade in other Asian currencies furthering this new paradigm.
Labels:
Coal,
Energy,
India Oil Imports,
Indian rupee,
Physical commodities,
Russia,
Trading
Location:
New Jersey, USA
Sunday, 7 August 2022
Two decoupled energy blocs with India and the Gulf in the middle
Australia’s Strategic Policy Institute opined on the emergence post Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, of two decoupled energy blocs with China and Russia on one side, and Europe, North America, and the Indo-Pacific democracies, on the other side. Prior to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, in 2020 almost 30% of EU crude oil imports came from Russia and over 40% of natural gas imports came from Russia while more than half of solid fossil fuel (mostly coal) imports originated from Russia (54 %). European nations are now seeking new sources of gas, oil and diesel fuel from the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, and India, as well as an increased focus on local energy production to wean themselves off Russian energy sources.
With Russian oil banned in the United States and Europe, India finds itself in the middle of the two decoupled energy blocs buying Russian crude at substantial discounts, powering its energy-thirsty economy at a lower cost, and refining into products like diesel and jet fuel to sell at better-than-usual margins abroad. Ironically, Europe is eager to buy the same Russian crude after it is refined in India into diesel shipping the fuel to Europe since March 2022, with increased trade flows expected over the coming months. China buys 50% of its oil supplies from the Gulf.
The Strait of Hormuz is the most important chokepoint between the two decoupled energy blocs accounting for about a third of the world’s sea-borne oil (and a fifth of the world’s total oil exports), linking oil and gas Upstream producers in the Middle East with Downstream consumers in Europe, North America, China and Indo-Pacific.
In 2016, according to America’s Energy Information Administration, the waterway carried some 19m barrels of crude and other petroleum products a day. This volume will accelerate through 2030 because of new mega refineries in the Gulf China and India and growing demand in Europe and emerging markets. According to Bloomberg, State-run Qatar Energy’s six new gas-liquefaction plants are set to produce 8 million tons of LNG per year for export to Europe. Morgan Stanley forecasts global LNG consumption to rise by 60% through 2030.
With Russian oil banned in the United States and Europe, India finds itself in the middle of the two decoupled energy blocs buying Russian crude at substantial discounts, powering its energy-thirsty economy at a lower cost, and refining into products like diesel and jet fuel to sell at better-than-usual margins abroad. Ironically, Europe is eager to buy the same Russian crude after it is refined in India into diesel shipping the fuel to Europe since March 2022, with increased trade flows expected over the coming months. China buys 50% of its oil supplies from the Gulf.
The Strait of Hormuz is the most important chokepoint between the two decoupled energy blocs accounting for about a third of the world’s sea-borne oil (and a fifth of the world’s total oil exports), linking oil and gas Upstream producers in the Middle East with Downstream consumers in Europe, North America, China and Indo-Pacific.
In 2016, according to America’s Energy Information Administration, the waterway carried some 19m barrels of crude and other petroleum products a day. This volume will accelerate through 2030 because of new mega refineries in the Gulf China and India and growing demand in Europe and emerging markets. According to Bloomberg, State-run Qatar Energy’s six new gas-liquefaction plants are set to produce 8 million tons of LNG per year for export to Europe. Morgan Stanley forecasts global LNG consumption to rise by 60% through 2030.
Labels:
Downstream,
EU,
European Economy,
Gulf,
India,
Oil trading,
Russia,
Strait of Hormuz,
Upstream
Location:
New Jersey, USA
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)