Throughout 2022 and early 2023, Indian refineries purchased Russian crude through Dubai-based intermediaries such as Hinera Trading, Black Pearl Energy Trading, Starex Trading, and Pontus Trading, as well as Dubai-based proxies for Russian NOCs Everest Energy, DMCC and Lukoil Litasco.
Indian rupees were utilized to bypass SWIFT for Russian oil payments, resulting in Russia accumulating surplus rupees in vostro accounts within India. By mid-2023, Russia ceased accepting rupees for energy trade, leading private Indian refiners to pay for Russian oil in Chinese Yuan while state-owned refiners paid in UAE Dirhams.
In 2024, the threat of U.S. sanctions complicated UAE Dirham transactions, consolidating the dominance of only three middlemen—Lukoil Litasco Middle East, Hinera Trading, and Black Pearl Energy Trading—as primary sellers of Russian crude to India.
A blog focused on educating global physical energy commodities participants on evolving financial, regulatory and marketing developments in the Asian commodities markets including use of cryptocurrencies in physical commodities trading. This blog seeks to educate market participants only and does not constitute financial advice.
Showing posts with label Indian rupee. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Indian rupee. Show all posts
Tuesday, 8 April 2025
Monday, 15 August 2022
New paradigm shift in India’s energy trade - evidence in charts
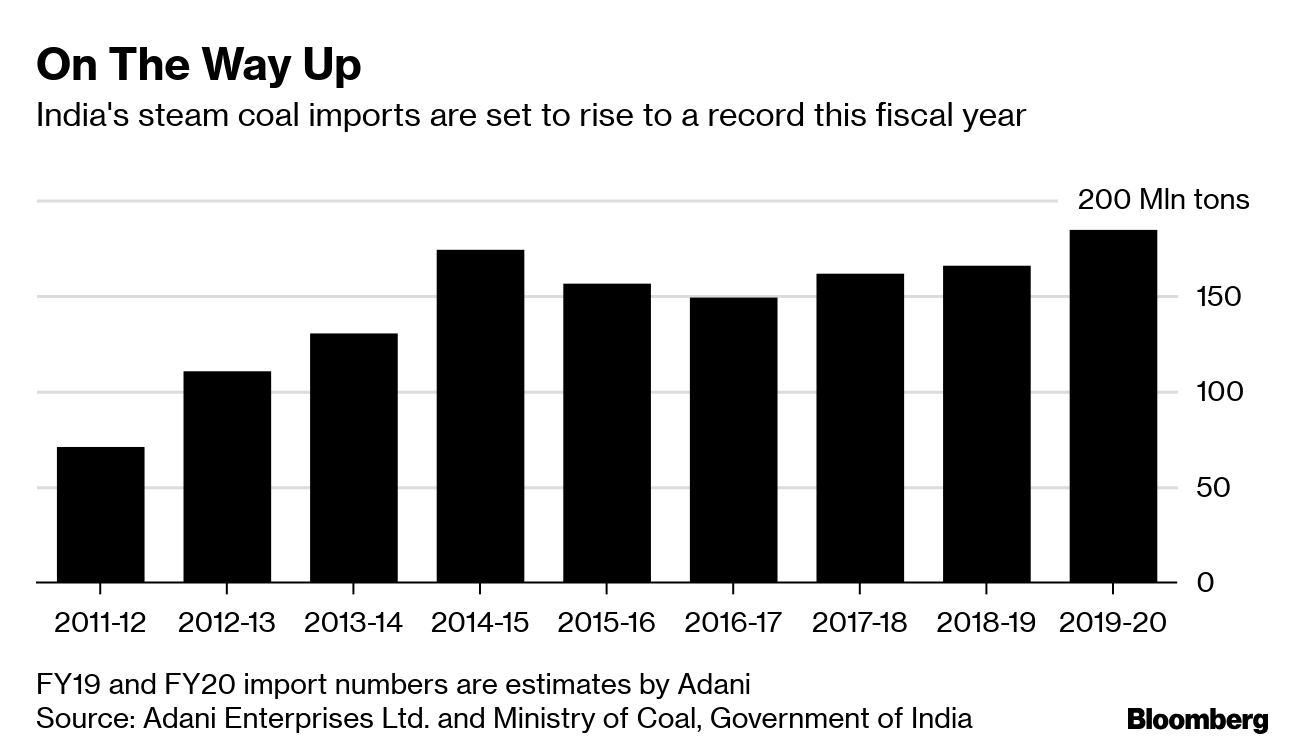
An unprecedented paradigm shift is evolving in the energy commodities trade of India, the world’s third-largest oil consumer after the US and China, and second largest oil importer after China importing over 85 percent of its crude needs. Despite being the second largest coal producer in the world, India is also the world’s second largest coal importer as new power plants designed to use only high grade imported coal (17.6 GW or 8.6% of the 204.9 GW installed power generation capacity) while older power plants import the fuel for blending with domestic coal according to S&P Global. Indian Ministry of Commerce’s Export & Import Data Bank (EIDB) points to crude oil imports worth US$ 122.45 billion and around 173.32 million tons of coal imports worth US$ 30.6 billion in the year 2021-22.
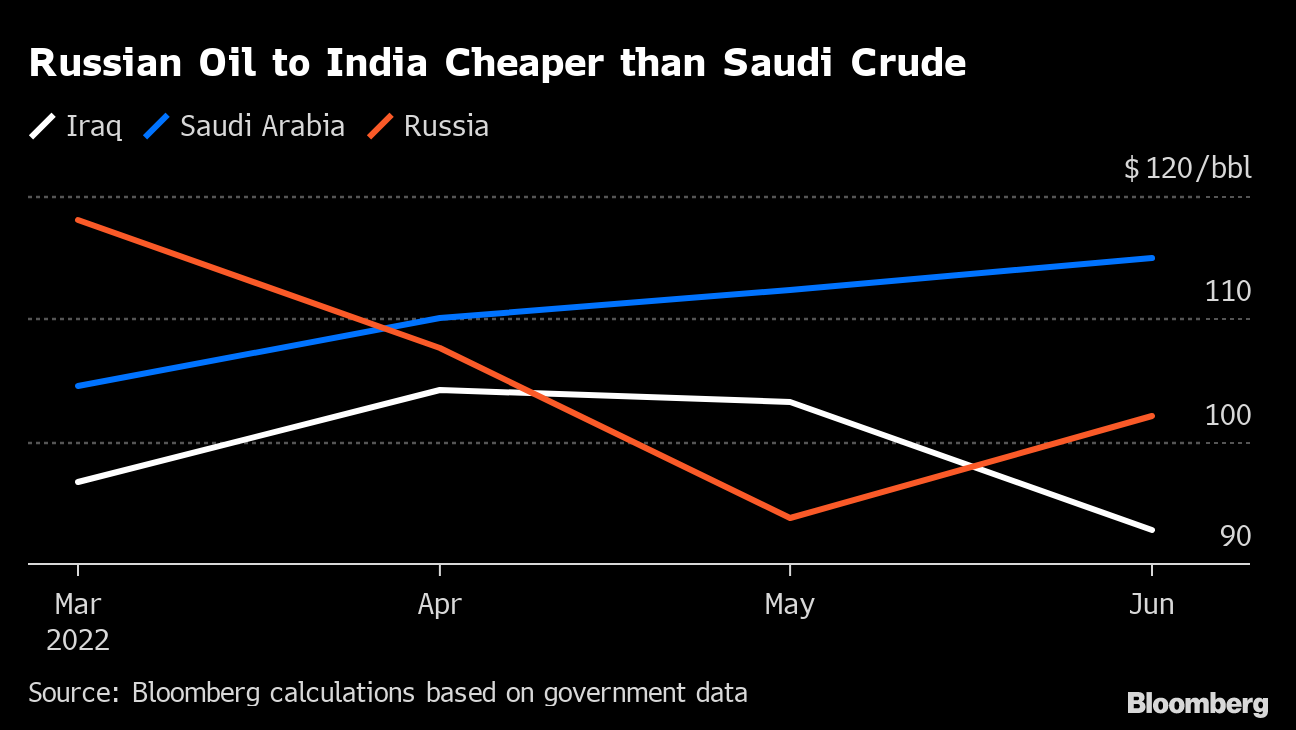
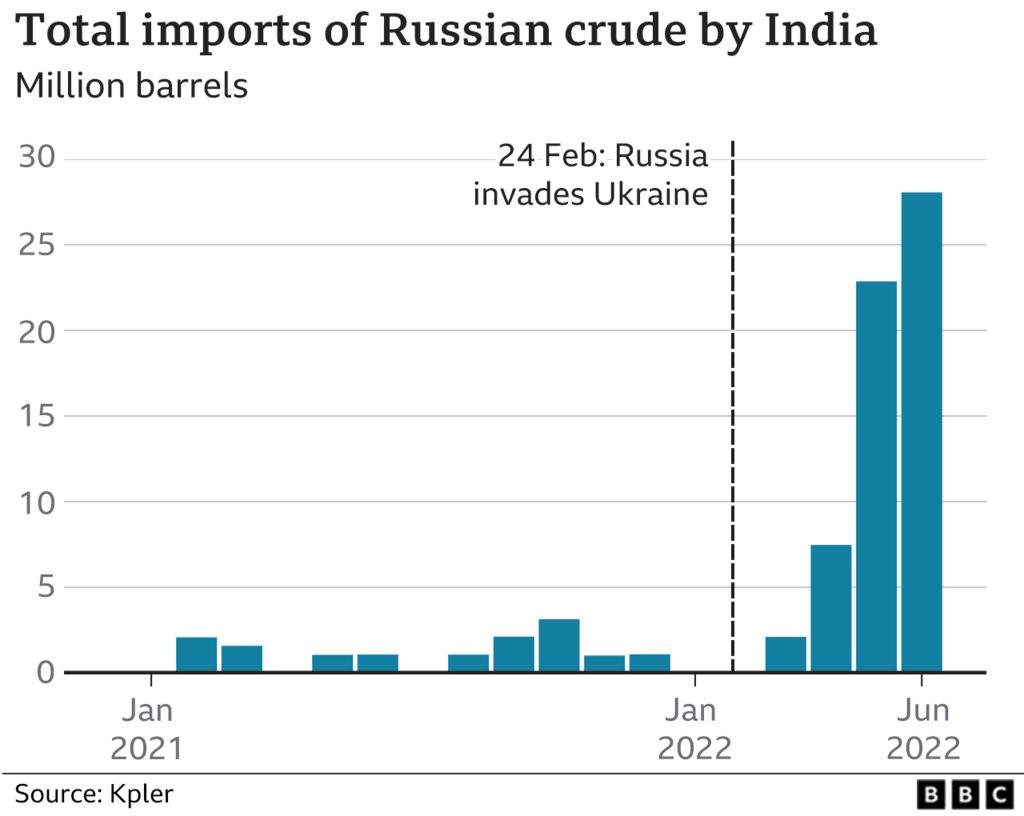
In a new paradigm shift, according to analysis by Bloomberg, Russia surpassed Saudi Arabia as the second-biggest supplier of crude to India in June 2022, ranked just behind Iraq.
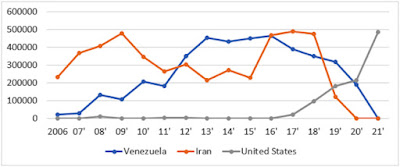
In comparison, India’s imports of U.S. oil and gas commodities which grew from $4.1 billion in 2018 to $5.5 billion in 2020 roughly halved by July 2021 and the US is no longer among India’s top oil suppliers according to the oil ministry’s Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell.
With economic growth expected to rise to 8% this year, Indian state refiners which dominate fuel retailing are in the market for the lowest priced crude that works with their refinery and product configurations via open tenders. The discount of Russian Urals crude to Brent crude was around $30 per barrel with bigger discounts to other medium-sour grades typically sold to India such as Oman and Upper Zakum reflecting the huge risk premium the market requires to transact on Russian cargoes according to Kpler. In 2021, only around 2% of India’s total oil imports (12 million barrels or 33,000 barrels a day on average of Urals crude) came from Russia, according to Kpler.
Urals oil contracts for India rose from nothing in January 2022 to 300,000 barrels a day in March to 700,000 a day in April totaling around 26 million barrels ending June 2022 according to Kpler. The India-bound Russian tankers head into Jamnagar, in the western state of Gujarat, where Reliance Industries has the world’s largest refinery complex, and into the Vadinar refinery of Nayara Energy an affiliate of Rosneft, the Russian state company which alone imports crude oil worth about $1bn every month or 400,000 barrels per day on average.
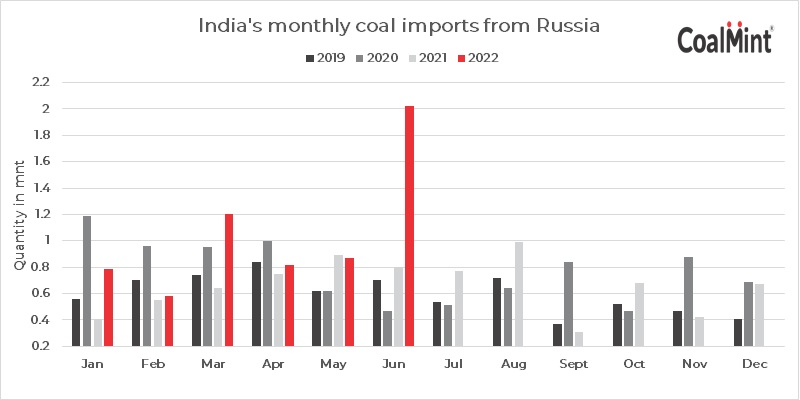
This paradigm shift in India’s energy trade is not limited to oil. Russia became India's third-largest coal supplier in July 2022 after Indonesia and Australia, with imports from Russia jumping 70.3% to a new record of 2.06 million mt, per Coalmint data. In comparison, thermal coal imports from the US fell 52% on the year to 3.4 million mt over the same time. Russian imports to India are expected to rise even higher due to a wider coal shortage during the third quarter of 2022 exacerbated by higher electricity demand. Steep discounts offered by Russian suppliers for thermal coal and Urals crude as global prices trade at near-record highs due to western sanctions are not the only reason for this paradigm shift. India is also exploring alternative payment channels for trade with Russia including allowing payments for energy commodities in the Indian rupee or settling the trade in other Asian currencies furthering this new paradigm.
This paradigm shift in India’s energy trade is not limited to oil. Russia became India's third-largest coal supplier in July 2022 after Indonesia and Australia, with imports from Russia jumping 70.3% to a new record of 2.06 million mt, per Coalmint data. In comparison, thermal coal imports from the US fell 52% on the year to 3.4 million mt over the same time. Russian imports to India are expected to rise even higher due to a wider coal shortage during the third quarter of 2022 exacerbated by higher electricity demand. Steep discounts offered by Russian suppliers for thermal coal and Urals crude as global prices trade at near-record highs due to western sanctions are not the only reason for this paradigm shift. India is also exploring alternative payment channels for trade with Russia including allowing payments for energy commodities in the Indian rupee or settling the trade in other Asian currencies furthering this new paradigm.
Labels:
Coal,
Energy,
India Oil Imports,
Indian rupee,
Physical commodities,
Russia,
Trading
Location:
New Jersey, USA
Saturday, 4 May 2013
India IT outsourcing industry may be spiraling downwards hurting India's GDP further
Changing US immigration legislation landscape, slowdown in capital spending on IT and competition from newer, cheaper sources of IT labor pool such as the Philippines and China is forcing the Indian IT outsourcing industry to metamorphosize into providing alternative models of outsourced services (see video). IT outsourcing has created more than 2 million jobs and in 2012 contributed 6.4% of India's GDP according to the National Association of Software and Services Companies, based in New Delhi. Already, IT outsourcing behemoths such as Infosys are being squeezed by revenue pressures and forced to try new strategies in an increasingly commoditised market. Unless a new paradigm shift in IT outsourcing occurs, Indian IT outsources may spiral downwards further hurting India's weak growth prospects. Investors are strongly cautioned to diversify away from IT outsourcing linked equities and increase their exposure to US dollar denominated assets.
Labels:
India economy,
Indian equities,
Indian rupee,
IT Outsourcing,
US dollar
Friday, 3 May 2013
Long term prognosis for the Indian Rupee is abysmal - time to increase exposure to US dollar denominated assets
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) clearly fears inflationary pressures in India to the extent that it cut the repo rate only by 25 basis points today disappointing markets. RBI governor is quoted in the Economic Times as saying that "Conditional upon a normal monsoon, agricultural growth could return to trend levels. The outlook for industrial activity remains subdued, with the pipeline of new investment drying up and existing projects stalled by bottlenecks and implementation gaps." Persistently high current account deficit, credit growth falling to the lowest growth rate in over a decade, and now the RBI's own admittedly hawkish stance on inflation only add to an abysmal prognosis for the fate of the Indian rupee. Expectations that the Rupee will hit 60 to the US dollar are steadily rising. Government Pollyannas still try to come up with creative explanations to invent a growth story (see video).
As long as the RBI's Liberalised Remittance Scheme is still available to Indian residents, Indian or NRI investors are strongly urged to increase their portfolio exposure to US dollar denominated investments. You only have yourself to blame if your net worth significantly falls due to a sliding Indian rupee.
Tuesday, 30 April 2013
Comparing FDI into India with inward migrant remittances paints a truer picture of where Indian economy is headed
India received a total of US$69 Billion in remittances from NRIs and other overseas Indians in 2012 making India the leading recepient of remittances from overseas. This covered almost 40% of the merchandise trade deficit in 2012. During the April-February period of 2012-13, FDI into India declined 38% to $20.89 billion as compared to $33.49 billion during the same period of the previous fiscal year. Sectors which received large FDI inflows during the 11 months of 2012-13 include services ($4.74 billion), hotel and tourism ($3.21 billion), metallurgical ($1.39 billion), construction ($1.26 billion) and Pharmaceuticals ($1.11 billion). India received maximum FDI from Mauritius ($8.97 billion), followed by Japan ($2.11 billion), Singapore ($1.98 billion), the Netherlands ($1.67 billion) and the UK ($1.06 billion). These figures paint a completely different picture of the Indian economy and where it is headed. Thank God for the migrant remittances, it is essentially helping reduce the Indian current account deficit (CAD).
Also, the fact that Mauritius is the leading FDI investor into India (which is essentially laundered money moving out of India and back into India through the Mauritius channel) tells us that the media hype we usually hear about all the FDI interest in India is essentially bogus. The falling FDI rate into India tells us that investor confidence in India still remains very low. Thus, it is essentially the migrant remittances that is keeping the Indian rupee afloat. If one day the migrant remittances start falling, India's CAD will balloon beyond repair and send the rupee into a free fall. For the next few months leading to Indian general election scheduled for 2014 very strong caution is advised.
Labels:
CAD,
Current Account Deficit,
FDI,
India,
India economy,
Indian rupee,
remittances
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)