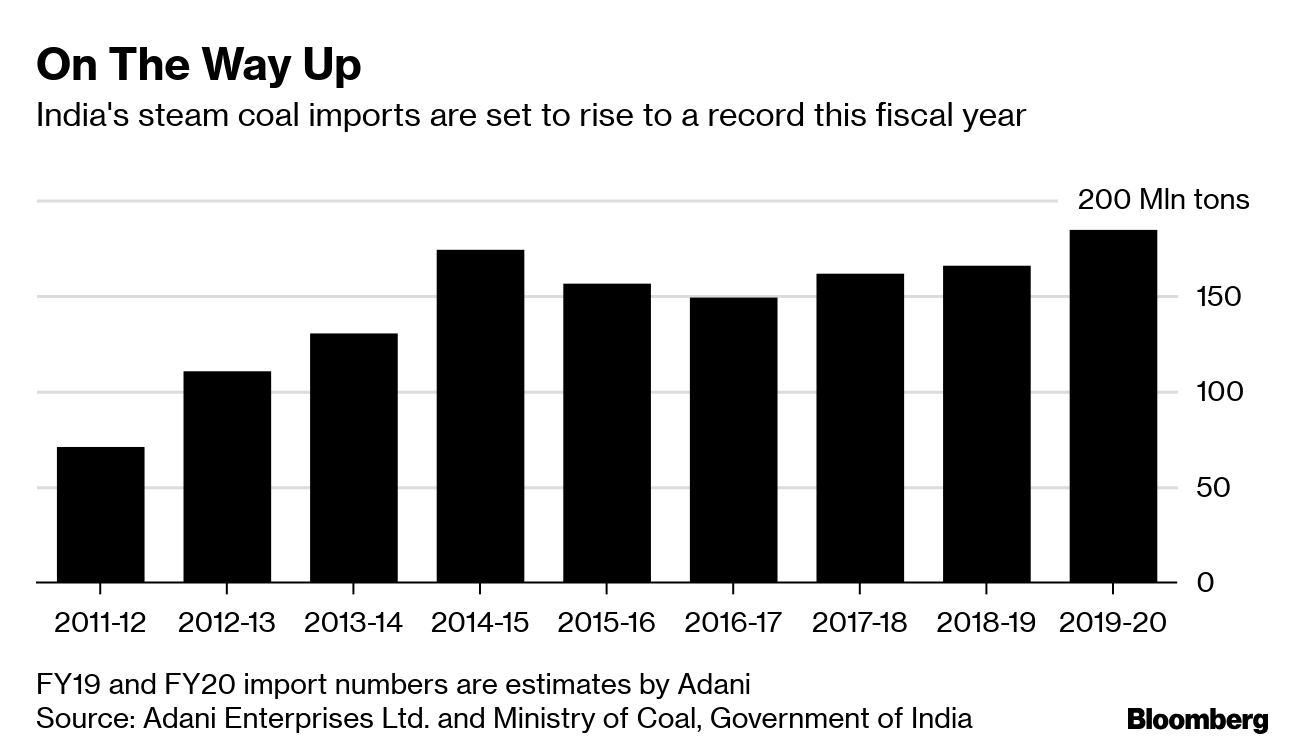
An unprecedented paradigm shift is evolving in the energy commodities trade of India, the world’s third-largest oil consumer after the US and China, and second largest oil importer after China importing over 85 percent of its crude needs. Despite being the second largest coal producer in the world, India is also the world’s second largest coal importer as new power plants designed to use only high grade imported coal (17.6 GW or 8.6% of the 204.9 GW installed power generation capacity) while older power plants import the fuel for blending with domestic coal according to S&P Global. Indian Ministry of Commerce’s Export & Import Data Bank (EIDB) points to crude oil imports worth US$ 122.45 billion and around 173.32 million tons of coal imports worth US$ 30.6 billion in the year 2021-22.
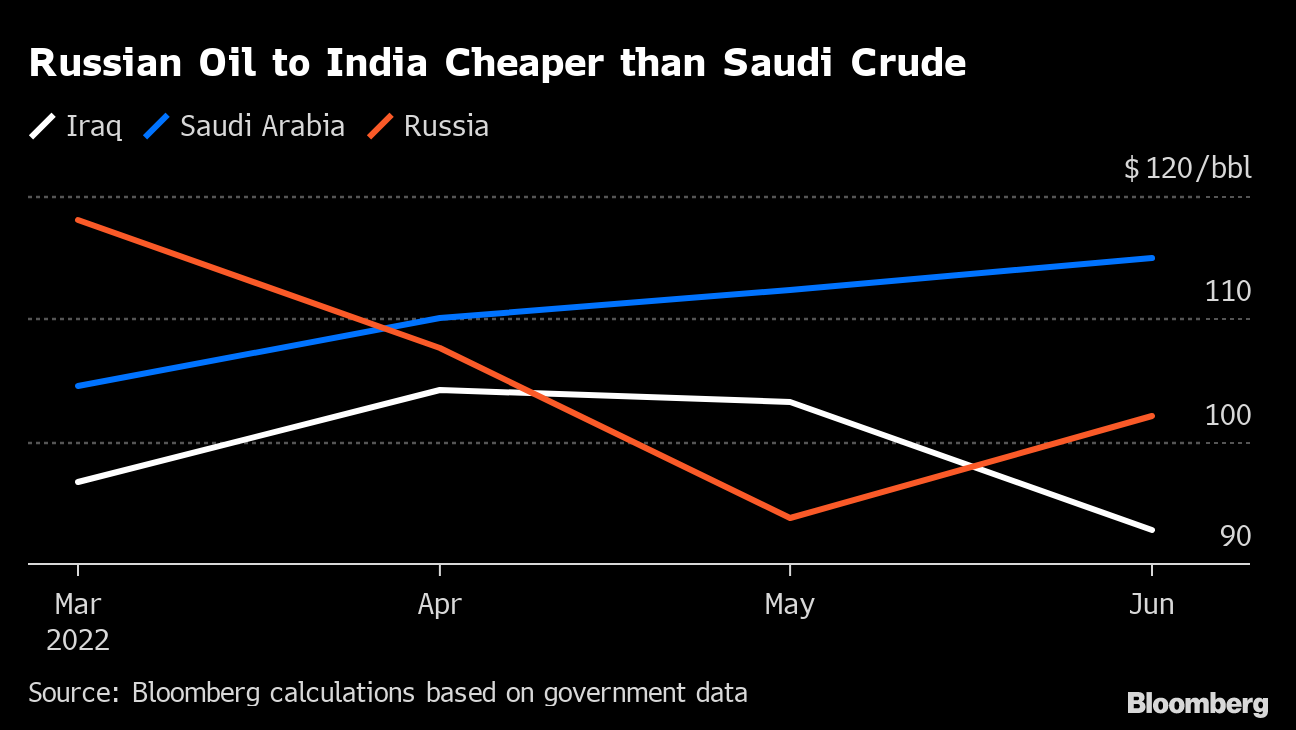
In a new paradigm shift, according to analysis by Bloomberg, Russia surpassed Saudi Arabia as the second-biggest supplier of crude to India in June 2022, ranked just behind Iraq.
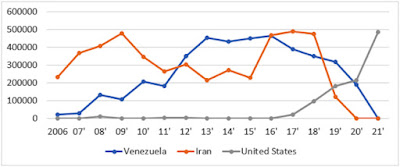
In comparison, India’s imports of U.S. oil and gas commodities which grew from $4.1 billion in 2018 to $5.5 billion in 2020 roughly halved by July 2021 and the US is no longer among India’s top oil suppliers according to the oil ministry’s Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell.
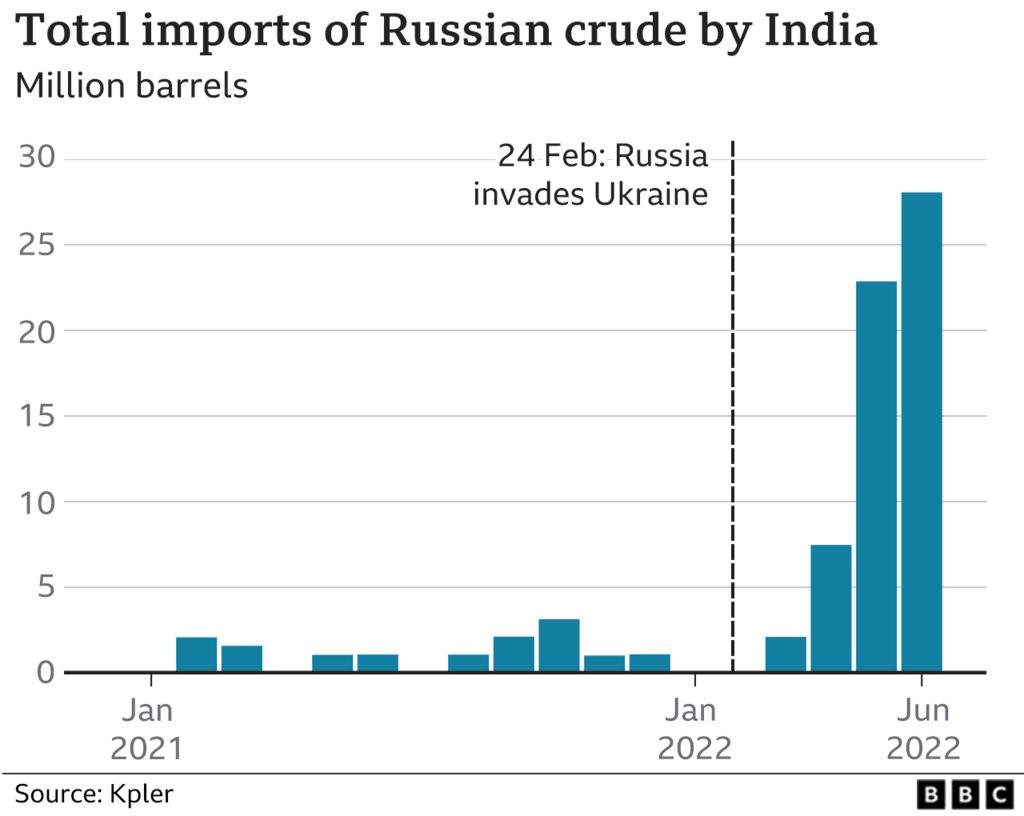
With economic growth expected to rise to 8% this year, Indian state refiners which dominate fuel retailing are in the market for the lowest priced crude that works with their refinery and product configurations via open tenders. The discount of Russian Urals crude to Brent crude was around $30 per barrel with bigger discounts to other medium-sour grades typically sold to India such as Oman and Upper Zakum reflecting the huge risk premium the market requires to transact on Russian cargoes according to Kpler. In 2021, only around 2% of India’s total oil imports (12 million barrels or 33,000 barrels a day on average of Urals crude) came from Russia, according to Kpler.
Urals oil contracts for India rose from nothing in January 2022 to 300,000 barrels a day in March to 700,000 a day in April totaling around 26 million barrels ending June 2022 according to Kpler. The India-bound Russian tankers head into Jamnagar, in the western state of Gujarat, where Reliance Industries has the world’s largest refinery complex, and into the Vadinar refinery of Nayara Energy an affiliate of Rosneft, the Russian state company which alone imports crude oil worth about $1bn every month or 400,000 barrels per day on average.
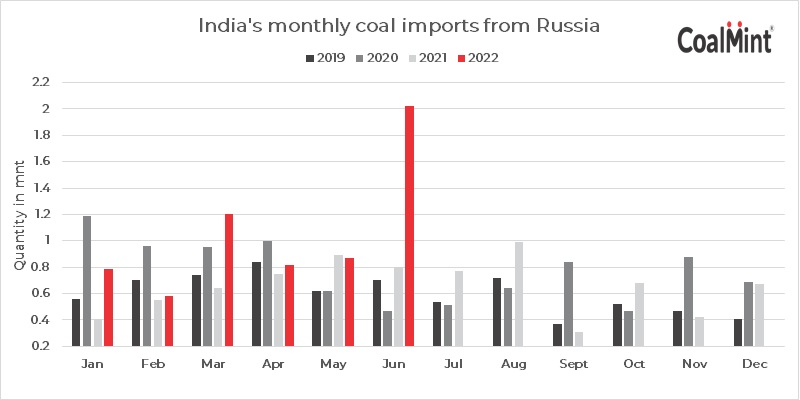
This paradigm shift in India’s energy trade is not limited to oil. Russia became India's third-largest coal supplier in July 2022 after Indonesia and Australia, with imports from Russia jumping 70.3% to a new record of 2.06 million mt, per Coalmint data. In comparison, thermal coal imports from the US fell 52% on the year to 3.4 million mt over the same time. Russian imports to India are expected to rise even higher due to a wider coal shortage during the third quarter of 2022 exacerbated by higher electricity demand.
Steep discounts offered by Russian suppliers for thermal coal and Urals crude as global prices trade at near-record highs due to western sanctions are not the only reason for this paradigm shift. India is also exploring alternative payment channels for trade with Russia including allowing payments for energy commodities in the Indian rupee or settling the trade in other Asian currencies furthering this new paradigm.
A blog focused on educating global physical energy commodities participants on evolving financial, regulatory and marketing developments in the Asian commodities markets including use of cryptocurrencies in physical commodities trading. This blog seeks to educate market participants only and does not constitute financial advice.
Showing posts with label India Oil Imports. Show all posts
Showing posts with label India Oil Imports. Show all posts
Monday, 15 August 2022
Wednesday, 29 December 2021
Dramatic shift in India's Oil import sources - from OPEC to non-OPEC
The world's third largest oil importer and consumer importing 85% of its crude, India continues to import crude from OPEC producers but a dramatic shift towards new non-OPEC sources seems to be under way as illustrated by these two charts from Reuters:
Back in October of 2021 India's Oil secretary had contemplated forming a group seeking to bring together state-run and private refiners to seek better volume based crude import deals. In November, India's crude imports reversed a declining trend to hit its highest level in 10 months. As reported by Platts, January through November 2021 saw India's oil product exports rise 3.2% on the year to 54.7 million mt, or 1.3 million b/d.
Labels:
Distribution,
Emerging Markets,
India Oil Imports
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)